how to fix packet loss
Packet loss: problems, causes and solutions
One of the most important metrics related to network performance, packet loss is a monitoring fundamental. So what's it all about?
The Oxford English dictionary probably defines 'loss' as a feeling of lack, missing something that was once in one's possession. Basically, loss has mainly negative connotations, except weight loss if you're on a diet. Packet is a container used for sending contents. If you lose the packet you also lose the contents.
At upper network layers, data travels in the form of packets, which deliver the information in a way that the receiver can order and use. Packet loss is when this information doesn't arrive correctly.
Packet loss issues
- Out-of-date information. Especially noticeable in real time situations, such as streaming services or online videogames. A few microseconds of delay can be the difference between capturing the flag in Counterstrike or being the ignominious recipient of a well-timed headshot; or, live-streaming the final of a sporting event and getting the result through your Twitter feed before witnessing it "live and direct".
- Slow loading times. Why is the webpage taking so long to load? Did I wake up this morning in 2005? Probably not, you're just another silent victim of packet loss.
- Loading interruptions. Wait, wait…still loading. Look, the progress bar has almost reached its destination at the top right of the screen. Just…two…more…seconds. If you add up all the time the Internet has cost humanity, waiting for pages to load, it adds up to over 25,000 years. Enough time for simple organisms to evolve new limbs or complex human civilizations to appear, peak and bottom out. Also, your email may not arrive.
- Closed connections. Remote servers for websites, file downloads, online videos, and so on, may end up closing their connections if the channel is open for too long without a clean, uninterrupted connection. This is usually a security measure, if that makes it any better.
- Missing information = websites that resemble a 90s Geocities page.
Why packets go missing
- Damaged hardware. Take your pick: damaged network card; deteriorated ports or connections, a bad router, or bad wiring in your office or building.
- Hardware capacity and bottlenecks. Sometimes, even though navigation speed is OK, and data is transiting smoothly through the network you still might find yourself dealing with hardware limitations. Imagine you contracted a higher velocity Internet connection, from 1GB to 10GB. However, your monitoring reports informs you that one of your devices is operating at 100% capacity for prolonged periods. If a node such as a switch doesn't have the capacity to correctly manage the volume of traffic it receives you're going to see a bottleneck.
- Network congestion. Information travels through multiple devices and links. If any of those points is maxed out a queue is going to form and the information pass through more slowly, and even get discarded if a certain amount of time has passed. Unlike bottlenecks, this kind of issue isn't restricted to a single node, but is a generalized problem.
- Wi-Fi. It's pretty normal for packets to be lost on Wi-Fi networks, as wireless networks are open to some unpredictable and/or uncontrollable elements, such as interference from other wireless networks, distance, thick medieval walls around Starbucks in Kraków, etc.
- Bugs in network devices. The software on your network devices may be corrupted, or buggy, so update it when necessary.
Monitoring packet loss
If you suffer any of these situations, you should be monitoring for packet loss. Using Pandora FMS and the packet_loss.sh plugin should give you the feedback you need to identify when and where your packets are bleeding out.
It works by pinging a remote component or element, such as an IP address, hostname or website, and checks whether there has been any packet loss.
When you deploy packet loss monitoring, you'll see a single module on the Pandora FMS console that contains all the information the plugin has collected, and allowing you to see at what time any packet loss occurred.
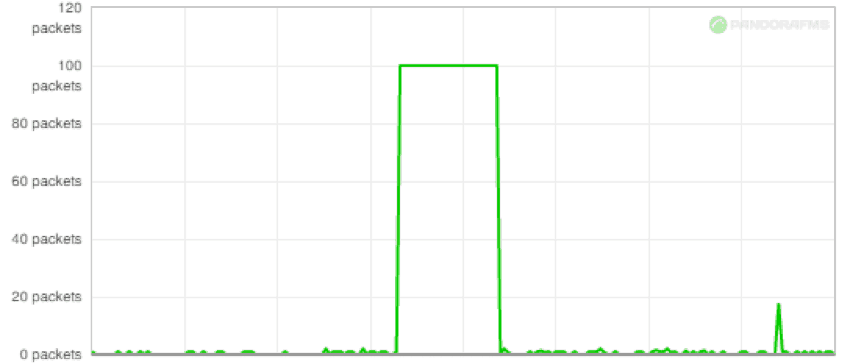
The graph below shows a loss of packets from an office's Wi-Fi Access point. Everything is fine but for one moment when the network experiences a severe loss of data packets. Using this information you can analyze the potential cause:
Looking at the graph representing packet loss on the Internet side informs us that there is constant packet loss, but that the values are low, indicating that there probably isn't another kind of problem implicated:
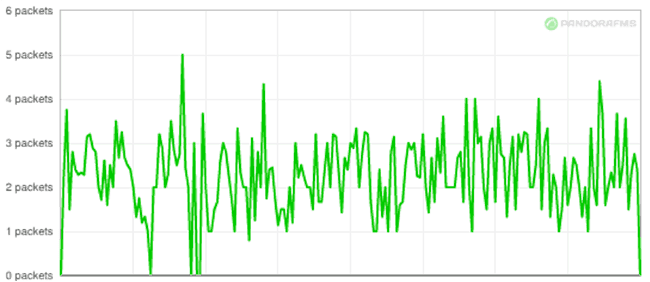
Once we've established that there is a loss of data, we can start to comb through the feedback, eliminating improbables and unlikelies, until we find a coherent solution.
In order to be able to contrast data, it's a good idea to monitor packet loss and latency times in parallel to find out if there's any correlation between slow latency times, and loss of data.
The following graphs show the correlation between latency in seconds (graph 1) and packet loss (graph 2):
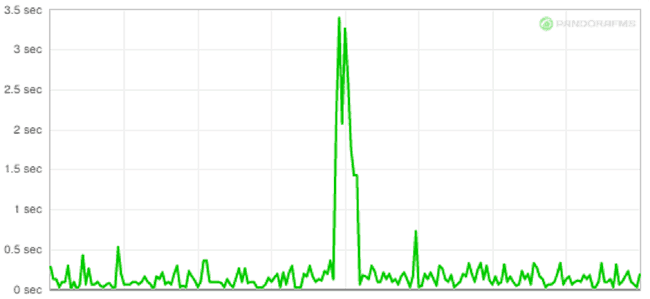
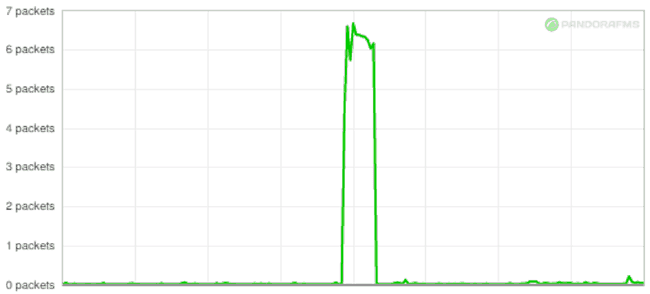
If you are interested in knowing more about the response and latency checks you can take a look at this video:
All this information can be presented in reports that combine graphs with data obtained through monitoring:
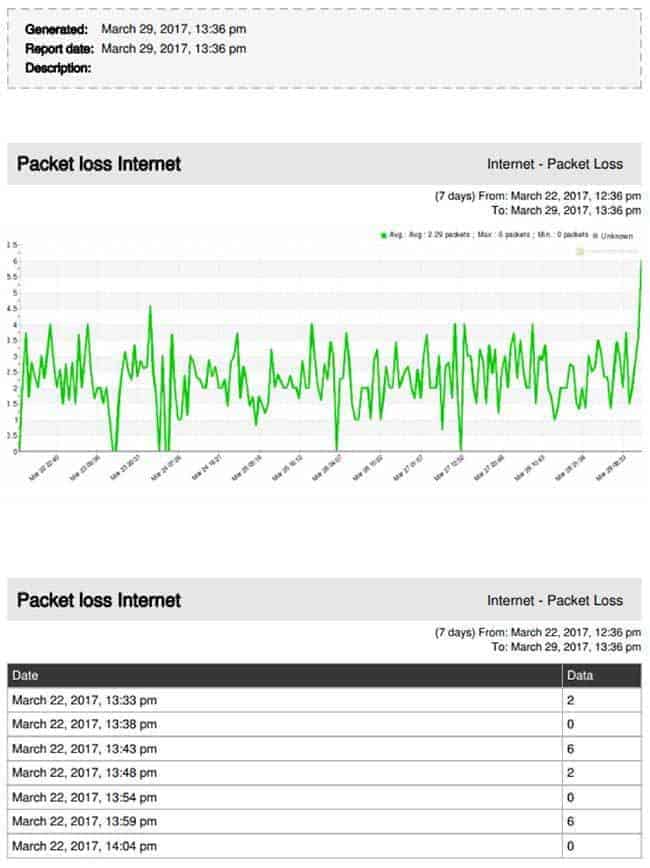
Packet loss remedies
There is no universal solution to this problem yet, as the causes of packet loss are varied. Here are some of the basic checks you can run in order to find out what is and isn't wrong.
- Check connections. Check that there are no cables or ports badly installed, or deteriorated.
- Restart routers and other hardware. A classic IT trouble-shooting technique.
- Use a cable connection. When in doubt, plug it in.
- Keep network device software up-to-date. In case of possible bugs in your OS or on your network devices keep all software updated. It's important to mention that if you've diagnosed packet losses from different pieces of hardware just updating your OS probably won't help as the problem is probably not on your hardware
- Replace defective and inefficient hardware. If you've run diagnostics on your network and it's still leaking packets you may just have to bite the bullet and head on down to the old computer store and upgrade your equipment.
About Pandora FMS
Pandora FMS is a flexible monitoring system, capable of monitoring devices, infrastructures, applications, services and business processes.
You can take a look at the network monitoring in Pandora FMS in the following video:
Would you like to know more about what Pandora FMS can offer you? Discover it by entering here: https://pandorafms.com
Or if you have to monitor more than 100 devices you can also enjoy a 30 days FREE DEMO of Pandora FMS Enterprise. Get it here.
Do not hesitate to send us your queries. The Pandora FMS team will be happy to assist you!
![]()
El equipo de redacción de Pandora FMS está formado por un conjunto de escritores y profesionales de las TI con una cosa en común: su pasión por la monitorización de sistemas informáticos.
Pandora FMS's editorial team is made up of a group of writers and IT professionals with one thing in common: their passion for computer system monitoring.
how to fix packet loss
Source: https://pandorafms.com/blog/packet-loss/
Posted by: mooreactoluesce68.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to fix packet loss"
Post a Comment